requests 库的基本使用
python爬虫从入门到放弃(四)之 Requests库的基本使用
基本使用
一个例子:
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")
print(type(response))
print(response.status_code)
print(type(response.text))
print(response.text)
print(response.cookies)
很多情况下如果直接使用 response.text 会出现乱码的问题. 而response.content 返回的数据格式是二进制格式,通过 .decode() 转换为 utf-8 就能解决:
print(response.content)
print(response.content.decode("utf-8"))
请求发出后,Requests 会基于 HTTP 头部对响应的编码作出有根据的推测。当你访问 response.text 之时,Requests 会使用其推测的文本编码。你可以找出 Requests 使用了什么编码,并且能够使用 response.encoding 属性来改变它:
response = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
response.encoding="utf-8"
print(response.text)
各种请求方式 request
requests 里提供个各种请求方式:
requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post")
requests.put("http://httpbin.org/put")
requests.delete("http://httpbin.org/delete")
requests.head("http://httpbin.org/get")
requests.options("http://httpbin.org/get")
GET
普通的 GET 请求很简单。
带参数 GET 请求,有 2 种方法:
- 对于 GET 请求,可以直接写到 url 中
- requests 允许使用
params关键字传递字典形式的参数,
注意:第 2 种方式中,如果字典中的参数为None,则不会添加到 url 上
response = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get?name=zhaofan&age=23")
data = {
"name":"zhaofan",
"age":22
}
response = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get",params=data)
添加 header 中的 user agent
在谷歌浏览器里输入 chrome://version 就可以看到用户代理,将用户代理添加到头部信息 headers ,就能模拟正常用户访问网站的请求:
headers = {
"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_4) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36"
}
response =requests.get("https://www.zhihu.com",headers=headers)
POST
通过在发送 post 请求时添加一个 data 参数,这个 data 参数可以用字典构造成:
data = {
"name":"zhaofan",
"age":23
}
response = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post",data=data,headers=headers)
print(response.text)
解析 response
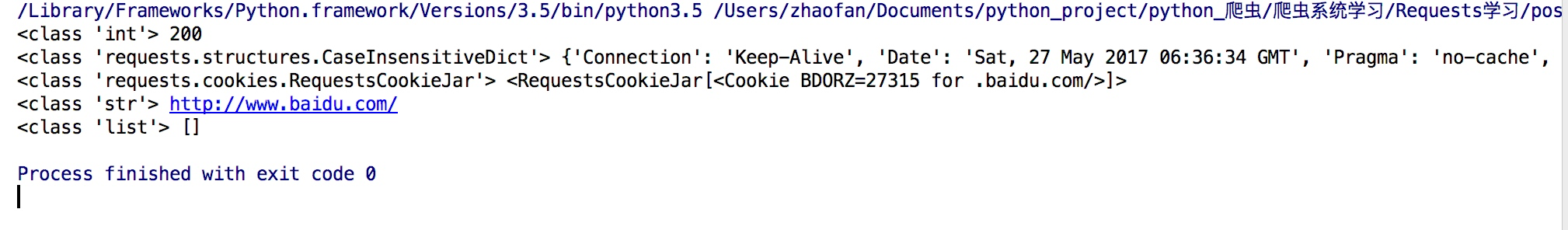
我们可以通过 response 获得很多属性,例子如下:
import requests
response = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
print(type(response.status_code),response.status_code)
print(type(response.headers),response.headers)
print(type(response.cookies),response.cookies)
print(type(response.url),response.url)
print(type(response.history),response.history)
结果如下:
解析 json
requests 里面集成的 requests.json() 其实就是执行了 json.loads() 方法,两者的结果是一样的。作用都是将 str 类型转换为 dict
import requests
import json
response = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get")
print(type(response.text))
print(type(response.json()))
print(response.json())
print(json.loads(response.text))
获取二进制数据
response.content 获取的数据是二进制数据,可以用于下载图片、视频等资源